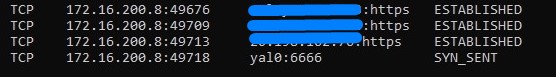
Malware uses port 6666 to do a call home action.
It attempts to avoid detection by excluding folders it uses in windows defender. It also interferes with antivirus program’s installation process.
It will attack SQL port 1433 on a list of server IP addresses provided by perpetrator.
Registry keys under HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\silsvc and HKLM\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\silsvc are not accessible nor able to take ownership of the keys and subkeys.
Doing netstat -anp tcp obtain a list of established port and it’s IP addresses will filter suspicious activities.
A second netstat -ano will list the suspicious ports with its process owner’s PID. With its PID known, tasklist | find “
If suspicious processes are found, they can be terminated with taskkill /F /PID “
These steps will disable some of the components loaded but there will be some services that will restarts itself as it is invoked by another malicious process.
A hex to text decode https://cryptii.com/pipes/hex-decoder may assist to decipher image path specified in registry keys.
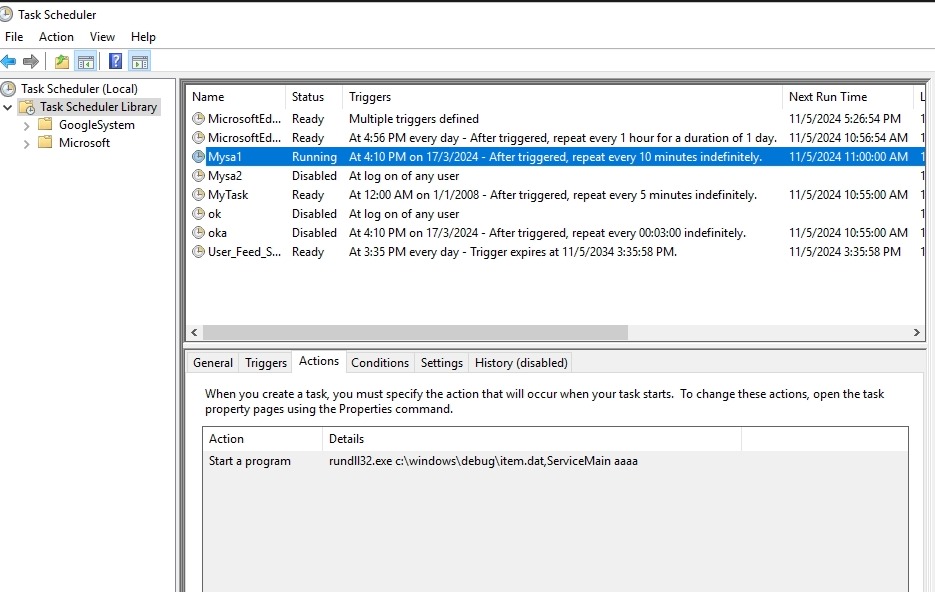
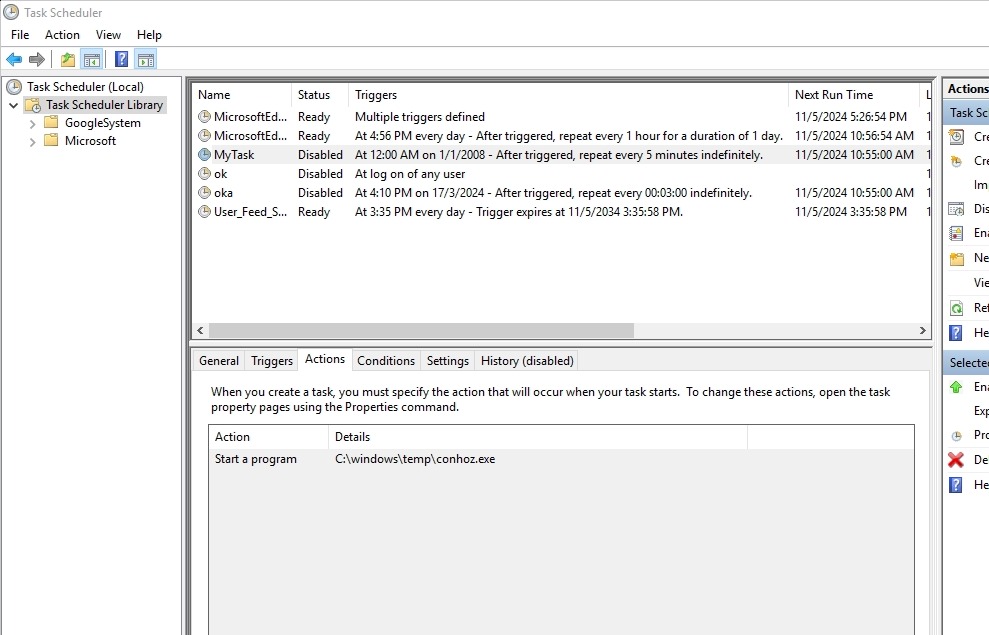
Check task scheduler and remove all instances of automated tasks added by malware. Details of each of these scheduled tasks will show where the payloads are located.
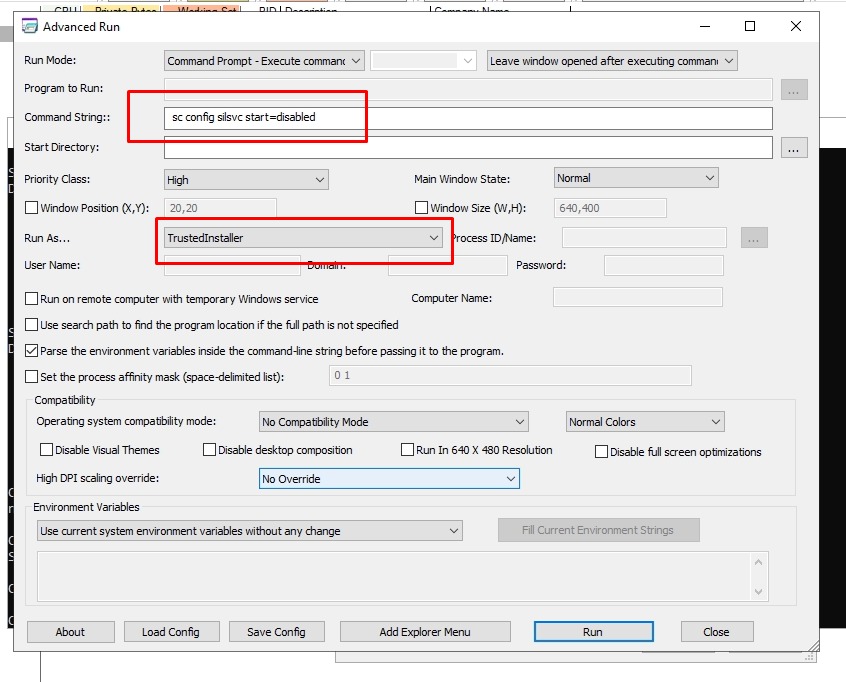
silsvc service will resolve to %SystemRoot%\system32\silsvc.exe but its registry keys are not accessible until regedit is ran under TrustedInstaller system account using AdvancedRun from Nirsoft.
Using CMD under account associated with TrustedInstaller, remove hidden/system attributes from silsvc.exe file using attrib -r -s -h silsvc.exe and rename it to .bak from .exe.
Start regedit and remove silsvc service under HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services and HKLM\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services. Always export/backup any entries prior to deleting it.
Also disable silsvc service from starting up using sc config silsvc start=disabled using TrustedInstaller account and reboot.
Seek alternative antivirus products like Dr Web Security Suite for cleaning folders excluded within Microsoft Defender configuration. (These exclusions were added by the malware and keeps reappearing until all hidden malware processes were terminated.)
If using Microsoft Defender, update your virus definitions and remove any folder exclusions added prior to doing a full scan. Remove any traces of the files that were created by the malware.
Redo the whole process until scan returns no more risks.
The location of the folders and files in this case were found at
C:\PerfLogs (lmsa22.exe, sqlservr.exe and miscellaneous text files.)
C:\Windows\system32 (silsvc.exe hidden, system attribute enabled)
C:\Windows\system (msinfo.exe)
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCache\IE (delete everything here)