
The dark web is a part of the internet that is not indexed by search engines like Google. The dark web is used for many illegal activities, such as drug dealing, pedophilia, and terrorism. The dark web is not the same as the deep web. The deep web refers to the majority of the internet that is not indexed by search engines. The dark web is a subset of the deep web.
The dark web is dangerous because numerous criminal activities take place on the dark web.
It’s a part of the internet that is not easily accessible to the average user. It can only be accessed by using a special browser, such as Tor or I2P. The dark web is also commonly referred to as the deep web, which is a part of the internet that cannot be accessed via a standard search engine.
The majority of content on the dark web is hosted on darknet markets. The darknet is a part of the internet that is not indexed by search engines, and is only accessible via darknet browsers. The darknet is also commonly referred to as the dark web or deep web.

Some common mode of infiltrating your system are used by cyber criminal when your information is known.
Phishing
Phishing is a technique used by hackers to gain access to your personal information such as your email accounts. This is done by sending emails that appear to be from a legitimate source.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts your files, and in some instances, your hard drive. Hackers then demand a ransom to unlock your files.
Doxing
Doxing is the act of obtaining sensitive information such as credit card numbers, passwords, and addresses from someone. This can be done by using tools such as phishing or search engines.
For example, if you’re infected with a trojan, it can capture your keystrokes, allowing the hacker to access your personal information.
A keylogger can also be used to steal your passwords for various accounts, including your email and social media accounts.
If you’re infected with a ransomware virus, it’s a little different, as this kind of malware will encrypt your files, making them inaccessible. The only way to regain access to your files is to pay the ransom, which is usually in bitcoin.
If you’re infected with malware that steals your personal information, your computer might be used to send spam emails to everyone in your address book. Depending on the type of malware, it can also steal your banking information, allowing a hacker to steal your money.
If you’re infected with a virus that makes your computer mine cryptocurrency, your computer will use your CPU to mine a cryptocurrency for the hacker. That means that your computer will be running slowly, because it’s using your CPU to mine cryptocurrency, instead of using it for the tasks you want it to do.
How Can I Protect Myself?
Keep your system updated. Updates patch vulnerabilities in your operating system and software. One way that malware infects a system through vulnerabilities.
Lookout for suspicious behavior in your system, example, system slowing down drastically, missing/new icons on desktop without installing any new programs, long list of running processes when you are not running any applications, heavy disk activities and even receiving bounced mails you did not send.
To check running processes, start by rebooting your system clean. To view tasks running, right-click on your computer taskbar, select Task Manager.
To view a list of outgoing or incoming connections to your system even in clean boot state, click Search or Start, type CMD then press Enter. (If you like to run as administrator, hold Ctrl and Shift before pressing Enter.)
Next type netstat -ano into command prompt and press enter.
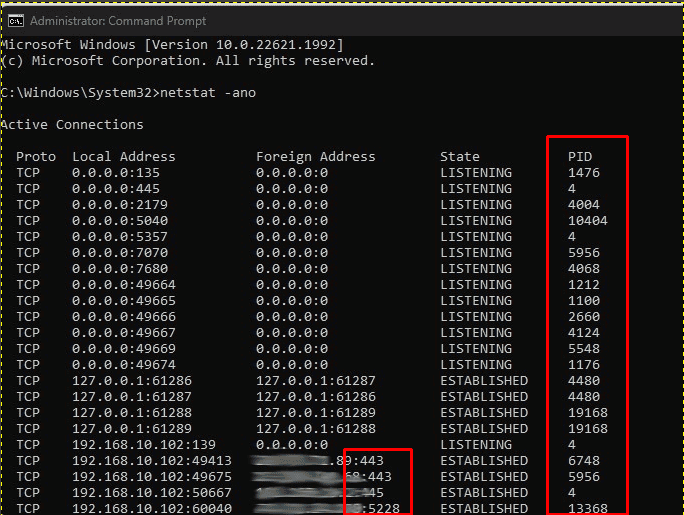
Take note of the processes (PID) and their listening ports (e.g. 443 above). These information is important if you want to dig further into finding out the owner of the process.
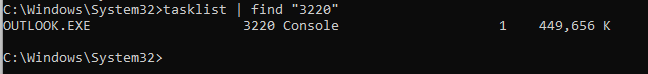
Next, use tasklist to find out the owner of a process which may be having a long list of connections.
In my case, the process I want to find was PID 3220, so I ran tasklist | find “3220” to filter out the others. It shows Outlook, which I did leave it running.
In cases where it is suspicious, where you want to kill off the process, before any malware removal attempts, you can run taskkill /PID {pid number} /F to kill off the process. A /F flag is required to force terminate the process.
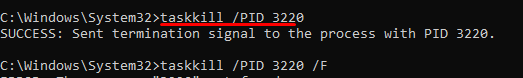
By killing off any suspicious malicious processes, it will ensure they do not interrupt any subsequent malware removal process running.
Some malware install themselves as rootkit, thus it starts as a system service and cannot be removed using the above method. In such instance, you may need to use other methods to clean it.
